

What is a noun? How does a noun work? A noun typically refers to a person, place, or thing. There are many types of nouns and plural forms of abstract nouns. For example, a concrete noun, which is a type of noun that is perceived the senses (taste, touch, smell) would be Apple. Nouns are an essential part of speech.
A noun is a word that identifies a place, thing, name, animal, or anything with an identity.A noun can be living, non-living, countable, non-countable, tangible, or non-tangible.
| Form | Definition |
| Noun | A noun is a word that names a person, place, thing, or idea. |
Deepen your understanding of nouns with a list of comprehensive noun examples.
Some nouns identify a person’s name, irrespective of their gender. Use these nouns to address a specific person.
Some nouns identify a place – a state, country, town, area, lane, apartment, street, or city. Or any location existing in the present, past, and future, reality or fictional world.
For example, Hill Valley (a fictional place in California) or the USA are nouns that name a place.
Nouns that identify intangible things – things that do not have a physical existence – are called abstract nouns.
Abstract nouns instead name a feeling, a perception, or a state of a being.
Abstract nouns rely on concrete nouns (nouns that have a physical existence) to complete their meaning.
Look at examples of abstract nouns in the given sentences.
A proper noun is a distinctive identity given to a noun. It always begins with a capital letter, irrespective of its position in a sentence. For example, Lucas and Maria stay in Germany.
On the other hand, a common noun is a group identity or a general identity given to a noun. They don’t begin with a capital letter. For example, A boy and a girl are studying Math.
Compare this list of examples to understand proper and common nouns better.
City of New York
There are three classifications for common nouns:
Concrete nouns identify a material thing. You can sense all the concrete nouns with human touch, sight, smell, taste, or sound.
Abstract nouns identify intangible and nonmaterial things. You can’t sense them directly, but you understand that it exists through external actions or signs.
For example, anger is an abstract noun. So you can’t see it directly but can gauge it through different (indirect) signs like a person yelling or throwing things forcedly.
Collective nouns identify a group of things or nouns—for example, a bush of thorns, a bunch of flowers, or a pack of spades.
Use collective nouns when you want to address a group of nouns as a unit simultaneously.
1 – Lock the door.
Here, ‘door is a common noun, but it’s not capitalized.
2 – Coffee is the best therapy!
Here, coffee is a common noun, and it’s capitalized since it’s the beginning word of the sentence.
Here are some more examples to determine the proper capitalization of common nouns.
A noun is also a subject. Therefore, you usually refer to the subject and construct the sentence around it.
Take the noun, Mandy, for example.
Here Mandy is the noun and the subject, and you construct the sentence around it by placing an action – cooking, and the object – sausages around it.
Take another noun, Melissa.
Here Melissa is the noun and the subject, and you construct the sentence around it by placing an action – leads and the object – content team at Blue House publishers around it.
For nouns as a subject, the noun used should be the performer of the verb in the sentence.
In Mandy and Melissa’s example, they are the performers of the verb ‘cooking’ and ‘leads,’ respectively.
A noun is also an object – direct or indirect. The ‘object’ is a noun at the receiving end of the verb. You usually refer to the object and construct the sentence around it.
Take the noun, laptop, for example.
Here, ‘laptop’ is a noun and an object – you construct the sentence around it.
Take another noun, bookshelf.
Here, ‘bookshelf’ is a noun and an object – you construct the sentence around it.
A complement is a part of a sentence that completes the sentence.
Nouns as a subject complement is a noun that complements the subject in a sentence. It acts as the adjective of the subject.
Here, ‘Andy’ is the subject, and ‘mechanic’ is the noun as a subject complement.
Here, ‘Robin’ is the subject, and ‘grapes’ is the noun as a subject complement.
Nouns as an object complement is a noun that complements the object in a sentence. It acts as the adjective of the object.
They call her crazy.
Here, ‘her’ is the object, and ‘crazy’ is the noun as an object complement.
An appositive noun (or noun phrase) immediately follows another noun or noun phrase to give extra details about it.
For example, My sister, Brenda, looks after the farm.
Here, Brenda is the appositive noun next to another noun, sister, and informs us about the sister’s name.
1 – A comma separates appositives that add extra information about a noun or noun phrase. You won’t change the sentence’s meaning even if you delete the ‘extra’ information.
Here, color is a noun, and red and black are appositive nouns.
2 – Don’t add a comma for appositives that add essential information about a noun or noun phrase. If you delete the ‘essential’ information, you will change the sentence’s meaning.
Here, pet is a noun, and lost is an appositive noun. If you remove the appositive noun, the sentence won’t make any sense.
A regular noun is any noun that forms plural by adding a -s or -es at the end.
For regular nouns ending with -x, -sh, -ch, -s, -z, or -ss, add an -es at the end of the word to form plurals.
Regular nouns that form plurals by adding -es
Regular nouns that form plurals by adding -es
Collective nouns identify a group of countable nouns—for example, team or audience.
Use a singular verb for a collective noun referring to a group as a unit.
For example, Joe’s family plans a vacation every new year.
Here, family is a collective noun representing a unit. So, use the singular verb plans.
Use a plural verb for a collective noun referring to a part that makes up the group.
For example, The Blue House students sing in the choir on Tuesday.
Here, students is a collective noun representing every student from the Blue House. So, use the plural verb sing.
Countable nouns are nouns you can count—for example, five numbers, one pen, and seven books.
On the other hand, uncountable nouns are nouns you cannot count—for example, water, rice, and air. So you can’t count them as one water, two rice, or nine air.
A verbal noun is derived from a verb but doesn’t act like a verb.
For example, ‘build’ is a verb, and ‘building’ is a verbal noun.
Verb Verbal Noun
Gender-specific nouns identify a masculine or a feminine noun—for example, man and woman. ‘Man’ identifies as a male, and ‘woman’ identifies as a female.
Use names to identify particular gender-specific nouns—for example, Sheldon and Melissa. ‘Sheldon’ identifies as a male, and ‘Melissa’ identifies as a female.
An attributive noun is a modifier that works as an adjective—for example, chicken soup. Here soup is a noun, and chicken is an attributive noun that provides extra details about the noun soup.
Plural nouns refer to more than one quantity of a specified noun.
Plural nouns are either regular or irregular nouns. To decide how to form the plural of a singular noun, look at the ending letters of the word and modify the noun accordingly.
Refer to our detailed guide on Irregular plural nouns here to eliminate confusion regarding plural nouns.
Possessive nouns show ownership. They usually have an apostrophe.
Here Tony is not a possessive noun.
Here Tony is a possessive noun.
An irregular plural noun follows different rules than simply adding a -s or -es at the end of a singular noun.
A noun phrase is a group of words that pose as a single noun.
The noun phrase is Ron and Edward, acting together as a single noun.
A noun clause is a group of words containing a subject and a verb and works as a single noun. It may or may not make complete sense by itself.
Further, a noun clause can be both a subject and object of a verb in a sentence.
Here, ‘whatever you recommend’ is a noun clause and works as a noun. The noun clause contains a subject ‘you’ and a verb ‘recommend.’
Here, ‘what you said’ is a noun clause and works as a noun. In the noun clause, you is the subject, said is the verb.







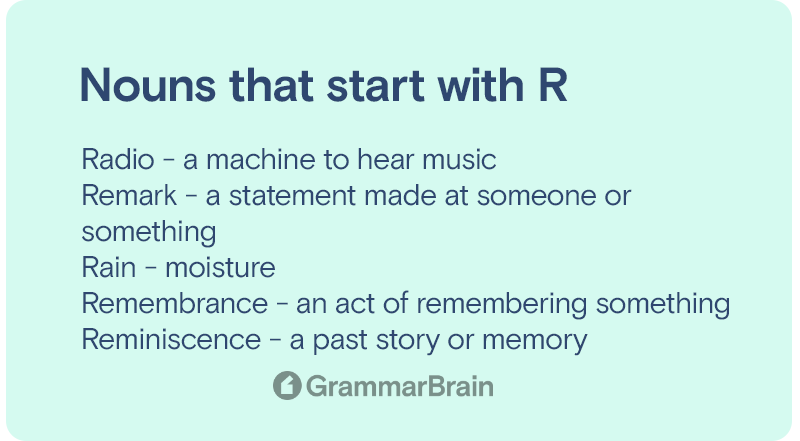







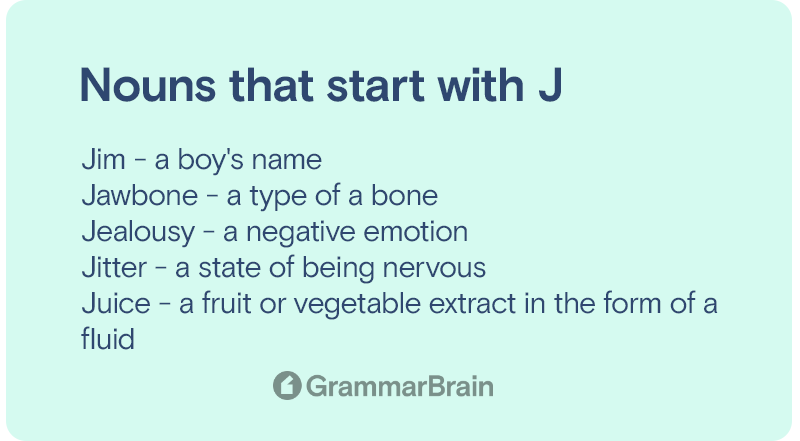
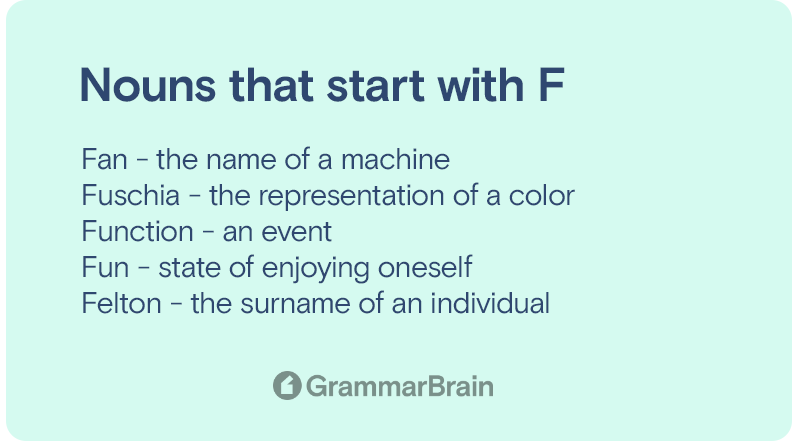
A noun that receives the action performed by the subject usually interacts with a direct object. When a noun that is the recipient of a direct object can also get referred to as an indirect object.
Does a pronoun name a person, place, or thing?Pronouns can identify a person. Although, they do not identify a place or thing.
What are proper nouns?Proper nouns are words that note names, like “America” or “Sam.” Proper nouns refer to a place or name.
Can nouns be plural or singular form?Yes, depending on how many there are (and countable or uncountable), will depend on how their plural form is used. Some nouns have a plural form identical to that of the singular: sheep/sheep.
How does a noun phrase work?A noun phrase functions in a clause or sentence to play the role of a subject, object, or complement of a verb or preposition.
What are mass nouns?Mass nouns are used after the words “a” or “an” or after a number.
What is an example of an abstract noun?“Courage” is a great example of an abstract noun. Courage cannot be seen or sensed. Although, we know that it exists.
Inside this article

Fact checked:
Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.